Waterwalls

Boiler waterwalls have always been among the most difficult challenges for design and life assessment, mainly because the failure modes appear to be outside the scope of design calculations. These notes identify some problem areas where progress has been made.
Waterwall Risk Management
Waterwall failures in supercritical boilers are generally regarded as the source of most forced outages. Failure modes are complex and involve combinations of severe environmental and thermal-mechanical conditions. Aggressive external corrosion after conversion to low NOx burner systems has been the main cause of waterwall tube failures and replacements in supercritical units. The response to this by utilities has been the use of coatings and Ni-based weld overlays to prevent wastage in the reducing combustion environment. While weld overlays have been generally successful in controlling wastage, other failure modes have occurred, such as:
- Extend time between repair and replacement
- Oxide cracking due to thermal-mechanical cycles
- Environmentally assisted creep-fatigue
- Fatigue at terminations of weld overlay and other poor field-welded details
- Overheating failures due to factors such as fouling which requires more attention on supercritical than on subcritical units.
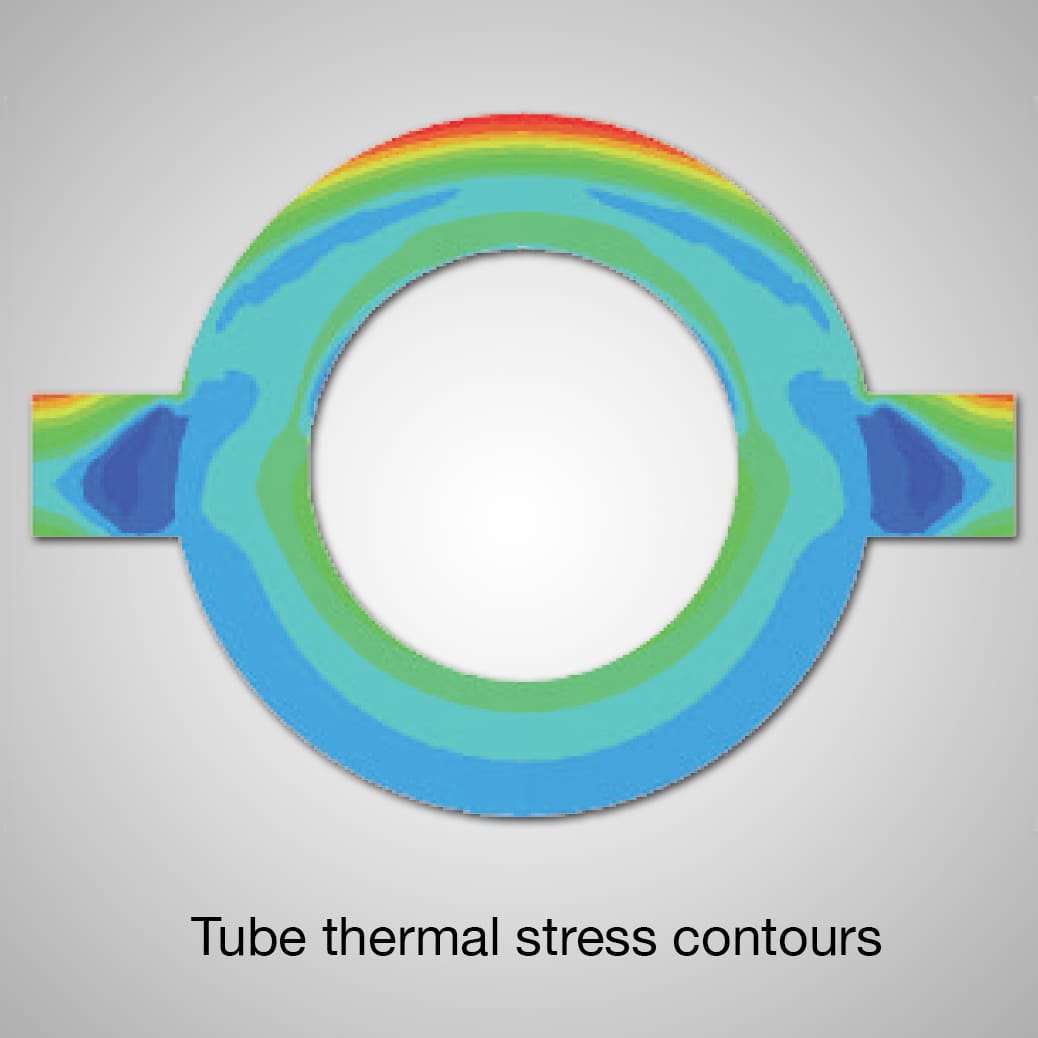
Circumferential Cracking
Environmentally assisted creep-fatigue due to severe thermal cycles has been identified as the cause of circumferential cracking, usually initiating at multiple sites on the crown of the tube. Both plain and overlaid tubes have suffered from such cracking. In addition to the environmental factors mentioned above, contributing factors are:
Frequent thermal cycling due to soot-blowing and slag falls
Internal fouling leading to elevated tube metal temperatures
Analysis of creep-fatigue damage using API/ASME data quantifies the thermal-mechanical contribution to circumferential cracking, and gives a basis for recommending limits to maximum heat flux and heat flux ranges.
Waterwall Failure Analysis & Troubleshooting
Waterwall Failure Analysis & Troubleshooting In addition to a metallurgical failure analysis, numerical models of failure increase the ability to manage and prevent failures. In most cases this will involve both environmental and thermal-mechanical effects. Managing the problem will require connecting the failure analysis to operational factors where possible. We provide:
- Tube failure analysis
- Creep-fatigue assessments based on heat flux cycles, for plain and weld overlaid waterwall tubes
- Recommendations for tube material upgrades
The complexity of tubewall failure analysis and life prediction requires a truly multidisciplinary approach. We have well-recognized capabilities in areas where metallurgical and thermal-mechanical failure modes interact, driven by combustion and fluid mechanics processes. The results are client-driven solutions beyond the scope of single-discipline approaches.
Our Capabilities
At Stress Engineering Services, we are dedicated to helping our customers solve their most difficult engineering challenges. We are experts in power generation and offer the following capabilities:
- API 579 Assessments
- Field Services & Monitoring
- High Energy Piping
- Materials Engineering
- Pressure Part Integrity
- Testing Services
Learn more about how we can help your organization, contact us today.



